In the realm of finance, rules-based money management plays a crucial role in guiding investment decisions and maximizing returns while minimizing risks. This strategy emphasizes the use of predefined rules and guidelines to streamline the investment process and achieve financial objectives efficiently. One key aspect of rules-based money management is security selection, which involves choosing specific investments that align with the overall investment strategy. In this article, we will delve into the intricate world of security selection rules and guidelines, exploring how investors can make informed decisions to build a robust investment portfolio.
1. **Diversification Strategy:** One fundamental rule in security selection is the emphasis on diversification. Diversifying an investment portfolio involves spreading out investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographical regions. This strategy helps reduce the impact of market volatility and specific risks associated with individual securities. By diversifying holdings, investors can enhance the stability of their portfolio and potentially achieve more consistent returns over time.
2. **Risk Assessment and Management:** Another critical aspect of security selection rules is conducting thorough risk assessments for potential investments. Investors should consider various risk factors, such as market volatility, industry-specific risks, and company financial health. By evaluating these risks, investors can make informed decisions about the suitability of a particular security for their portfolio. Additionally, implementing risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders or utilizing options for hedging, can help mitigate potential losses and protect capital in volatile market conditions.
3. **Fundamental Analysis:** Fundamental analysis is a cornerstone of security selection rules that involves evaluating the intrinsic value of a security based on factors such as financial performance, market position, and growth prospects. By analyzing a company’s financial statements, management team, and competitive landscape, investors can gauge the overall health and potential future performance of a security. Fundamental analysis provides valuable insights that can guide investment decisions and help investors identify undervalued or high-potential securities for their portfolios.
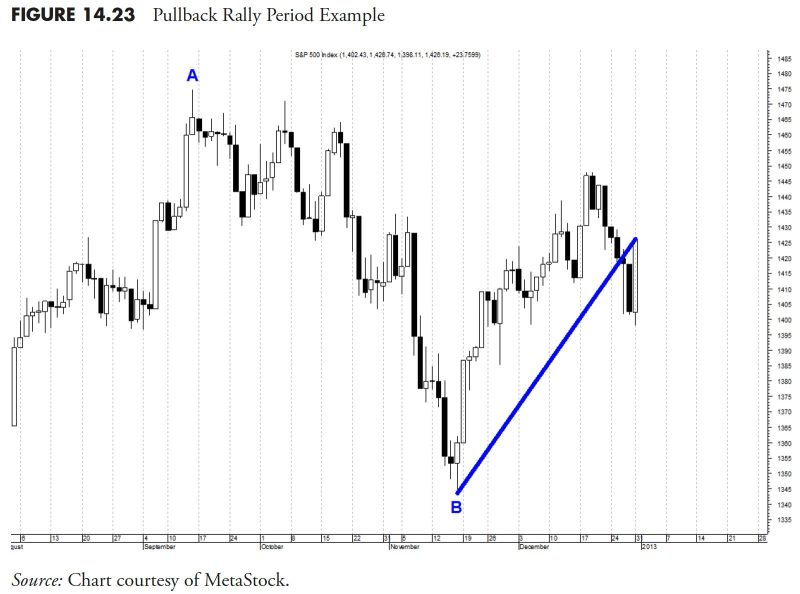
4. **Technical Analysis:** In addition to fundamental analysis, technical analysis is another essential tool in security selection rules. Technical analysis focuses on studying historical price movements and volume patterns to forecast future price trends. By analyzing chart patterns, indicators, and market sentiment, investors can gain valuable insights into potential entry and exit points for a security. Integrating technical analysis into the security selection process enables investors to make more informed trading decisions and optimize their entry and exit strategies for maximum profitability.
5. **Long-Term Perspective:** Lastly, a key guideline in security selection rules is maintaining a long-term perspective when evaluating investments. Rather than focusing on short-term market fluctuations, investors should assess the underlying fundamentals and growth potential of a security over an extended time horizon. By adopting a long-term investment outlook, investors can ride out market volatility, capture compound returns, and build a resilient portfolio that withstands market cycles and economic uncertainties.
In conclusion, security selection rules and guidelines form the bedrock of a successful rules-based money management strategy. By emphasizing diversification, risk assessment, fundamental and technical analysis, and a long-term perspective, investors can make informed decisions to build a resilient and profitable investment portfolio. By adhering to these security selection rules, investors can navigate volatile markets, manage risks effectively, and achieve their financial goals with confidence and precision.