In recent years, inflation has been a topic of concern for many economists and policymakers. The constant increase in prices of goods and services has a significant impact on the economy, consumers, and businesses alike. Various data sets and indicators suggest that inflation is not going away anytime soon, posing challenges for central banks like the Federal Reserve (Fed).
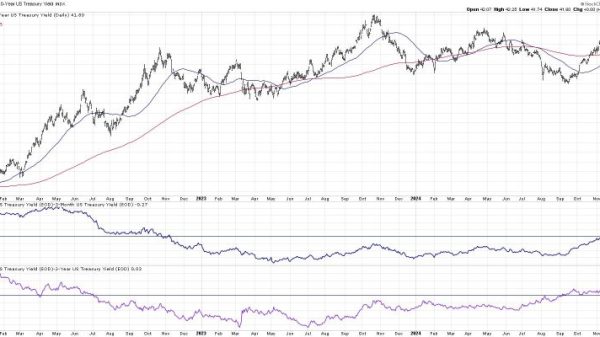
One key indicator that highlights the persistence of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI measures the average change in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services over time. Recent data reflects a steady rise in the CPI, indicating that inflationary pressures are on the rise. This upward trend in consumer prices is fueled by various factors such as supply chain disruptions, increased demand post-pandemic, and rising labor costs.
Additionally, the Producer Price Index (PPI) provides insights into inflationary pressures at the wholesale level. The PPI tracks changes in the selling prices received by domestic producers for their goods and services. Recent data on the PPI points to elevated price levels across various sectors, signaling that inflationary forces are widespread throughout the economy.
Another critical factor contributing to persistent inflation is the housing market. Home prices have soared in recent months, driven by low mortgage rates, limited housing supply, and increasing demand for larger living spaces amid the work-from-home trend. The rapid appreciation in home values has contributed to overall inflationary pressures and raised concerns about affordability for prospective buyers.
Furthermore, the labor market dynamics play a crucial role in shaping inflation trends. The tightening labor market, characterized by labor shortages and wage pressures, is causing companies to raise wages to attract and retain workers. As labor costs increase, businesses may pass on these higher costs to consumers in the form of higher prices, further fueling inflation.
In response to the persistent inflationary pressures, the Federal Reserve faces a challenging task of maintaining price stability while fostering sustainable economic growth. The Fed employs various tools such as interest rate adjustments and monetary policy to keep inflation in check. However, the delicate balance between supporting economic recovery and controlling inflation remains a challenging task for policymakers.
In conclusion, the data so far indicates that inflation is not likely to recede anytime soon, posing challenges for central banks globally. By closely monitoring key indicators such as the CPI, PPI, housing market trends, and labor market dynamics, policymakers can better understand the drivers of inflation and implement appropriate measures to address this economic challenge. Vigilance and proactive measures will be essential to navigate through the current inflationary environment and ensure a stable economic outlook for the future.